In a new recurring feature, the Observer showcases university labs and departments that have advanced integrative science. In the inaugural installment, APS Fellow Qi Wang talks about Cornell University’s Department of Human Development, which she chairs.
What is the history of the department? What was its genesis?
The Department of Human Development at Cornell University is an interdisciplinary entity that uses multiple approaches, methods, and levels of analysis to study human development across the lifespan and integrates basic and translational research to enhance development and well-being in diverse contexts and populations. The department distinguishes itself with an ecological view of development as unfolding in multiple overlapping contexts. It has consistently been ranked as one of the top human development programs in the country.
The department, founded in 1925, was one of the first departments in the United States established by a university that focused on child development within the context of the family. Over the past 90 years, the mission of the department has expanded to include the full lifespan: Adolescence and emerging adulthood were added to early childhood development during the 1960s, and adulthood and aging were added during the 1980s. The study of contextual influences has expanded outside of the family to a greater number and variety of contexts, including peer groups, schools, neighborhoods, and workplaces. The faculty have come to include scholars of multiple disciplines and methodologies. Currently, the department has a professorial faculty of 24. Undergraduate majors typically number between 250 and 300, with approximately 35 masters and doctoral students in residence.
How has it evolved over the years?
The department has become increasingly dynamic and integrative. It has maintained its ecological focus, exemplified by the influential work of APS James McKeen Cattell Fellow Urie Bronfenbrenner, APS Past Board Member Steve Ceci, and others, and in the meantime has redefined the ecological perspective to align with the development of the general field. This is reflected in our study of an increasing number and variety of contexts and their interactions with developmental (social, cognitive, biological) processes across the lifespan. We increasingly emphasize interdisciplinary and integrative approaches that span areas of psychology (cognitive, developmental, clinical, social, cultural), along with law, neuroscience, sociology, education, and history. We recently recruited a computational political scientist who studies social networks, political communication, online social support, and health. The department also has evolved to increasingly focus on culture and diversity, examining basic developmental processes in relation to a variety of demographic factors including socioeconomic status, gender, race and ethnicity, and cultural background.
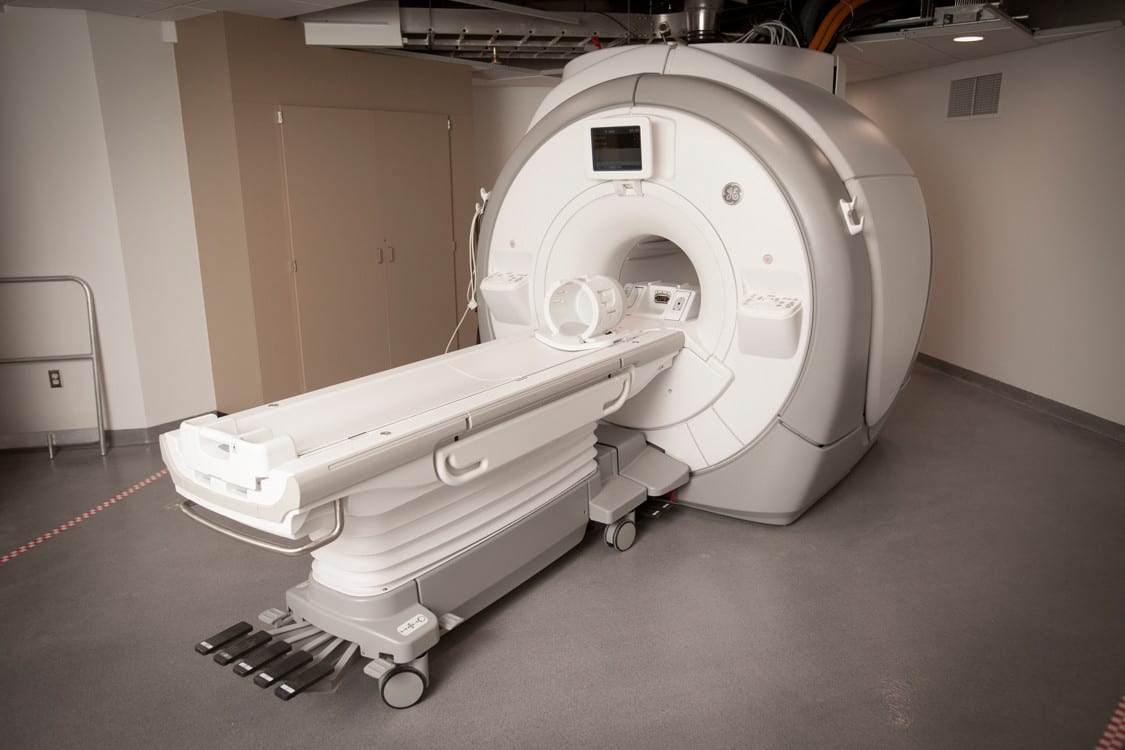
Our interest in advanced methodologies is reflected in the addition of neuroscience, biological/life sciences, and data science in the department and in the importance we place on multiple levels of analysis. From the sociology and psychology of health and aging to the neuroscience of memory, emotions, and decision-making, the department mixes equally observational and correlational studies with rigorous experimental approaches and interventions within and outside the laboratory. The department has made a strong investment in neuroscience, being the only human development program in the country to house an MRI facility. The department is also unique among human development programs in housing a nonhuman animal laboratory, allowing us to lead examinations of lifespan developmental changes in the brain and behavior and how they are shaped by diverse environmental contexts, early life experiences, and genes and their expression. The recent addition of social networks research and data science further extends our interdisciplinary strengths.
The department embraces translational activities and “use-inspired research,” seeking evidence-based solutions for real-world problems. Both its pedagogy and outreach are research-based — often research conducted by the very faculty member teaching a particular course or engaging in a particular outreach activity.
How many faculty members are in the department? What departments or disciplines are represented?
The department has consistently attracted a distinguished faculty. Many mainstream psychological scientists have decided to join our faculty, with four of our newer faculty leaving tenured positions at top psychology programs. In the past year, we have recruited four assistant professors who are among the very best of their cohort. Several members of our faculty hold National Academy memberships, including the National Academy of Education, the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, and the National Academy of Medicine. Members of our faculty have garnered just about every prestigious award within psychological science, including the APS William James Fellow Award, the APS James McKeen Cattell Fellow Award, the G. Stanley Hall Award, the Society for Research in Child Development Senior Distinguished Contributions Award, and the E. L. Thorndike Award. The department has a professorial faculty of 24, from various disciplines within psychology, sociology, political and information science, and neuroscience.
The research topics of the faculty fall into three general areas: Law and Human Development (LHD), Health and Wellbeing (HW), and Cognition in Context (CC). All areas are characterized by interdisciplinary focus, lifespan perspective, cultural diversity, multiple approaches, methods, and levels of analysis, and integrative basic and translational research to study real-world problems.
The LHD area assembles a group of world-class psychologists and legal scholars to study the interplay of law, psychology, and human development. It offers a top-notch PhD–JD dual degree program. The HW area houses leading research on typical and atypical development across the lifespan in diverse populations. Faculty in this area examine the relation between mental and physical health in response to contextual factors and have produced groundbreaking and policy-shaping work. The CC area offers the most dynamic and rigorous investigations of the developing mind in interaction with a variety of biological, social, and cultural factors. Faculty conduct research using neuroimaging, EEG, cross-species modeling, field and laboratory experiments, and longitudinal designs to understand fundamental processes underlying human mind and behavior in context.
What would you describe as the most surprising or unexpected collaborations that psychological scientists have been able to join or lead within the department?
Every generation brings new scholars from diverse disciplines to our department. Their research transforms the department into new directions and in the meantime also is transformed by the interdisciplinary culture of the department. Often they collaborate across disciplinary lines. One example is an outstanding young neuroscientist we hired, who began a collaboration with a sociologist in HD who studies aging. It is the sort of collaboration that would be unlikely in a homogenous setting. There are many similar instances of cross-disciplinary collaborations to study machine learning, affective neuroscience, decision-making, and so forth, within and outside of the department. The disciplines that have been involved in HD faculty’s collaborative research include law, particle physics, mathematics, microbiology, biomedical engineering, business, behavioral economics, communication, and information science.
Here are some of the current cross-disciplinary collaborations of our faculty:
- A cognitive developmental scientist is working with a sociologist from Cornell’s sociology department and a particle physicist at the Fermi Lab in Batavia, Illinois, to conduct a study on women in science.
- A cognitive developmentalist is working with a law professor at the University of Michigan on children’s testimonial competence.
- A sociologist is working with a team of physicians and health-care providers to conduct intervention research and policy analysis related to aging and health care, using evidence-based methods to develop a competent, caring, long-term care workforce.
- An HD neuroscientist is working with an HD sociologist on Alzheimer’s disease research.
- An HD member has had a long-term collaboration with a professor of pediatrics at another university around the evaluation of outcomes associated with the Nurse Family Partnership program.
- A member of HD collaborates with a member of our business school faculty on cultural influences on bias.
- A sociologist has been collaborating with both a pediatrics professor and an epidemiologist to examine the impact of poverty-related stressors on the cognitive and physical development of children in low-income families. She also works with two members of the Communications Department at Cornell to develop social-media use for health care among older adults.
- Another member works with a pediatrician/public health scholar in another university on the projected behavioral impacts of global climate change.
- An HD neuroscientist collaborates with a microbiologist here on the gut–brain axis and the biome.
- Faculty from an education department, a mathematics department, and a veterinary school have also worked with our faculty members.
Has forming an interdisciplinary entity such as this made it easier or more challenging to obtain grant funding and get research published?
Our interdisciplinary focus has made us more competitive in obtaining grant funding and getting the research published. Specifically, our research often cuts across the more traditional categories of psychology and amplifies their applied nature.
On the one hand, our faculty has demonstrated “mainstream” excellence. Our publications appear in all of the top specialty psychological journals and the top general–general journals. Our faculty also frequently publish in top specialty journals in nondevelopmental core areas of psychology. In addition to the research being of the highest quality, a key reason for our success in publishing is that our research targets theoretical and empirical questions that our peers perceive as important, no matter whether they do or don’t fit into intuitive categories.
On the other hand, our faculty also excel in many integrative and interdisciplinary publishing outlets and make broad scholarly contributions beyond their core areas and beyond psychological science. Our publications also appear in nonpsychology journals such as those focused on sociology, education, anthropology, and medicine, and as a result our work has reached vastly different audiences. In addition to peer-reviewed articles in journals outside psychology, our faculty have also published a range of influential books, op-ed pieces, and Chronicle of Higher Education articles that address a wide range of audiences. Oftentimes, building a reputation for solid work in core psychological science journals opens up opportunities for important broader contributions.
Part of the “translation” and “interdisciplinary” process is collaborating with colleagues outside the disciplines in which we were trained. There are many good examples in our department as noted earlier. Pertaining to publication, for example, several faculty have collaborated with researchers in medical fields and published in major health-related journals with high impact factors, including The Journal of the American Medical Association, Pediatrics, Annals of Internal Medicine, New England Journal of Medicine, and the American Journal of Public Health.
What are the strategies that the department has utilized in maintaining its top-rank position in the field?
One strategy is related to our hiring priorities. We hire the best people available through open searches, without constraints based on current research areas or rank. We also actively seek opportunities to hire targeted senior faculty who are superstars in the field. We are fortunate to have a very supportive dean who lets us conduct open searches and prefill lines with strong candidates and who does not rescind lines after unsuccessful searches. In addition, our faculty overwhelmingly support hiring the best people, regardless of area.
Another strategy is to self-reflect on our current research topics and to allow the department to evolve as scholarship and policy needs change. Over the years, there have been important shifts in research emphases as fields have either changed direction or ceased to exist with faculty retirement or leave.
Another effective strategy is to establish a mentoring system for junior faculty. Each nontenured junior faculty in the department is provided with a mentoring committee as soon as he/she arrives on campus. The committee consists of three tenured faculty whose research is in a similar area as that of the junior faculty. The committee provides honest and constructive written feedback to the mentee at the end of each year, which is then discussed with the mentee in person as well as reported to the general faculty. The feedback acknowledges the mentee’s achievements in research, teaching, and service and in the meantime helps the mentee identify any issues so they can be effectively addressed early on. Because of this supportive system and because we strive to hire the best people in the first place, our junior faculty have been extremely successful in their work. Many have come to be leading researchers in their respective fields. We have four APS Rising Stars, and many junior faculty have received young investigator awards from major organizations. In the past 15 years, we have not had a single case of denied tenure.
 CNN.com, "Loneliness peaks at three key ages, study finds -- but wisdom may help," December 19, 2018, by Susan Scutti
CNN.com, "Loneliness peaks at three key ages, study finds -- but wisdom may help," December 19, 2018, by Susan Scutti
 A total 340 San Diego County residents between the ages 27 and 101 participated in the study. Jeste and his co-authors hypothesized that these community-dwelling participants, none with serious physical or psychological ailments, would report more loneliness in old age based on the "usual assumption that as people get older, they become more alone," he said. They were surprised when they discovered two peaks (during the late 20s and mid-50s) in addition to the one in the late 80s. The results do not explain the reasons why people feel lonely, but Jeste had his theories.
A total 340 San Diego County residents between the ages 27 and 101 participated in the study. Jeste and his co-authors hypothesized that these community-dwelling participants, none with serious physical or psychological ailments, would report more loneliness in old age based on the "usual assumption that as people get older, they become more alone," he said. They were surprised when they discovered two peaks (during the late 20s and mid-50s) in addition to the one in the late 80s. The results do not explain the reasons why people feel lonely, but Jeste had his theories.